
How to Get Landscape Design Rendering: DIY or Hiring a Pro?
A landscape rendering gives you a 3D preview of your garden or yard – a chance to see every angle before any work begins. And it has gone digital. What


Contributing Writer | Architecture & Design Writer
A plot plan is a drawing required for any project you plan to undertake on your parcel of land.
It’s an essential part of legal documentation for property development.
To help you understand plot plans, we created this article to answer all your questions about their unique characteristics.
Table of Contents
Toggle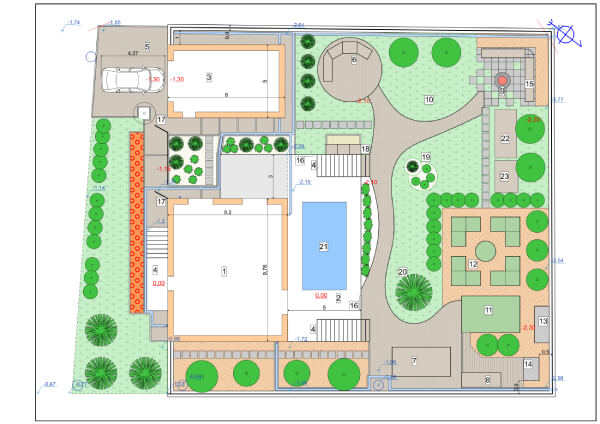
A plot plan is a detailed diagram of your property that illustrates the relationship between your house, any additional structures, and the surrounding land.
The blueprint’s purpose is to show key elements such as building layout clarity and positions (more on those later), providing a comprehensive overview of your parcel and proposed work.
And even though plot plans are also called site plans and people tend to use these two terms interchangeably, they have different meanings as there are slight differences when comparing a site plan vs a plot plan.
One of the differences is the requirements and usage of the plot plan.
You need a plot plan when you’re adding any kind of structure, attached or detached, to a piece of land or when you need to define property boundaries.
Therefore, the plot plan:
Therefore, a plot plan is essential during various stages of a construction project, including both residential and commercial planning, for processes such as:
By taking a look at various plot plan examples and drawings, you can gain a better understanding of how they assist contractors, builders, and architects in assessing property constraints and dimensions.
Now, let’s look at the different plot plans for specific uses.
Plot plans can vary depending on their purpose, usage, and level of detail.
Here are the most common plot plan types:
Here’s a detailed explanation of each type of plot plan and how they are used in various projects.
Residential plot plans are designed for homes or housing developments, showing the layout of buildings, garages, driveways, and gardens. They also indicate setbacks, helping homeowners understand building limits. While similar to residential site plans, plot plans typically focus on property boundaries and structure placement.
Residential plot plans are essential for permits and project planning.
Commercial plot plans provide a complete layout for business properties, detailing building locations, parking areas, driveways, and loading zones. These plans also address setbacks, utility lines, and pedestrian access to comply with zoning and safety standards.
Commercial plot plans are important for setting up a well-functioning commercial site.
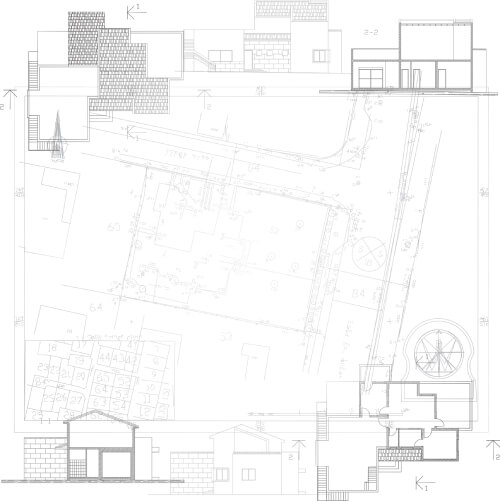
An architectural plot plan primarily focuses on the layout and design aspects of the property. It showcases structures, landscaping, and property orientation. This plan is usually created during the early design phase to communicate the property’s aesthetic and functional layout.
A construction plot plan is more detailed and used as a practical guide during the construction phase. It includes specific dimensions, site elevations, grading, and utilities to help builders precisely follow zoning and building codes.
A plot plan must include essential details to meet the requirements of government institutions that review and approve projects on your parcel of land. In our article “How to Read a Plot Plan” you can get insight into how to decipher the components.
To ensure your plot plan is accurate and complete, it should include the following components:
This is preliminary work, as you should first write the creation date of the plan and the address of the property it represents.
A key purpose of a plot plan is to provide an accurate depiction of the property and any proposed changes.
To achieve this, it’s crucial that all measurements are precise and drawn to scale, including a scaled layout of buildings and infrastructure.
The plans should start by delineating the property lines with clear boundary markers, then work inward to detail the location and size of all structures and features.
Each item on the plan should be clearly labeled, such as ‘house’ or ‘garage.’
A plot plan should show property features such as houses, outbuildings, pools, decks, patios, and driveways.
Utility lines and infrastructure information should also be found on the drawing, including:
Understanding their locations is crucial for construction planning and safety.
Plot plans must also include setbacks that are defined by local ordinances or HOA regulations. Setbacks dictate how far surveyed structures must be from the property line.
For example, in Phoenix’s R1-6 residential zoning district, setbacks are generally 20 feet at the front, 25 feet at the rear, and 10 and 3 feet on the sides [1].
For road frontage, these are typically 30 to 40 feet, while for other property lines, they can range from 5 to 10 feet.
After establishing all the essential structures and noting the relative distances, it’s time to incorporate comprehensive topography and elevation details.
This aspect is crucial for builders and designers to ensure that drainage patterns remain undisturbed.
If relevant to the proposed changes, the design includes the topography details, as well as any trees, shrubs, and bushes present on the site.
Access points, such as gates, pathways, and driveways, should be found on the plot plan to indicate how people and vehicles enter and exit the property.
Proper planning of these access points along with easements for external access is crucial for ensuring traffic flow, safety, and compliance with local regulations.
Additionally, besides easement for external access, it should also show any other easement that may be on the property (e.g., utility easement or drainage easement).
Finally, it’s essential to include instructions for interpreting your plot plan. The legend should explain the symbols used and clarify the orientation of the drawings to ensure it’s clear how to read the plot plan and prevent any confusion.
The easiest way to understand all the elements that are included in a plot plan drawing is by seeing them, so let’s take a look at some plot plan samples.
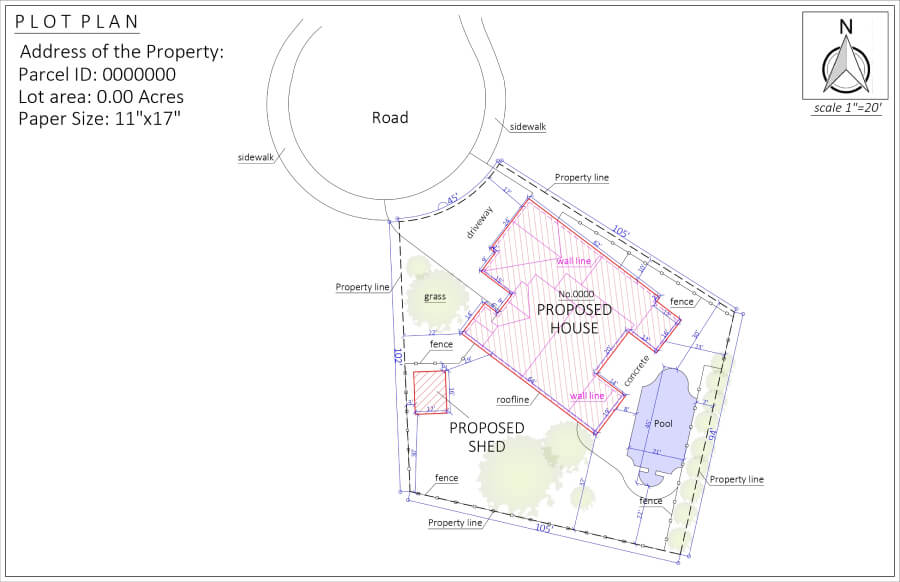
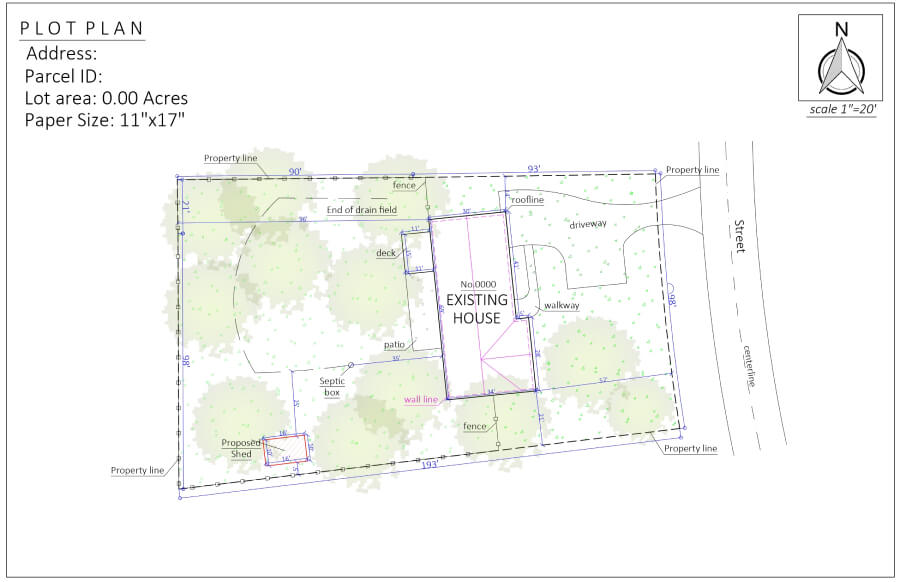
As you can see, all the elements of a plot plan are clearly visible on the drawing. These plot plan examples include proposed structures.
These samples show that plot plan drawings can be used for bigger projects, such as building a house, or a very small ones, like building a shed. But every drawing has the main elements of a plot plan, like the layout of the property and its features, such as slopes, pools, streets, etc.

To create a plot plan, you have to gather all the necessary information about your property and then start drawing, choosing between hiring a pro or undertaking a DIY project.
Engaging a professional designer, such as a surveyor or architect, can yield a certified plot plan with precise representations of property parcels.
However, since obtaining a certified plot plan is not a requirement in most jurisdictions, the expense of hiring a professional may be an unnecessary cost for your project.
A more affordable option for creating a plot plan is to draw it yourself, either by hand or with software.
However, before embarking on this task, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with local zoning laws and building codes and remember that a plot plan must be accurate enough to clearly represent property boundaries, existing structures, and the proposed layout of new constructions.
Each area has specific regulations concerning setbacks and land use, making compliance essential for obtaining permits and avoiding legal complications.
Nevertheless, utilizing software is a recommended DIY method, as many design software options—both free and paid / desktop or online—are available for drawing a non-certified plot plan.
Yet, be aware that you will need to invest time (and money) to learn how to use these tools effectively, which can be challenging if you need a plot plan quickly.
Redraw services provide the convenience of ordering a plot plan online, typically delivered within 24 hours.
These services are staffed by experienced professionals who make plot plans remotely, resulting in significantly lower costs compared to hiring an on-site professional.
Therefore, if your project requires zoning approval, ordering a plot plan for a permit online from GetASitePlan is likely the fastest and most cost-effective option.
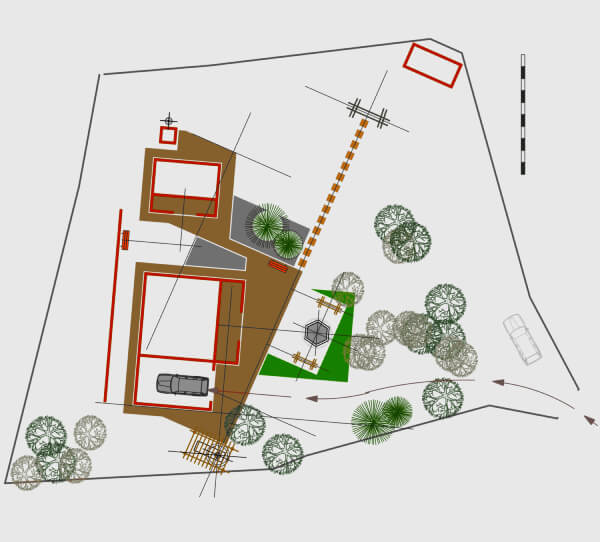
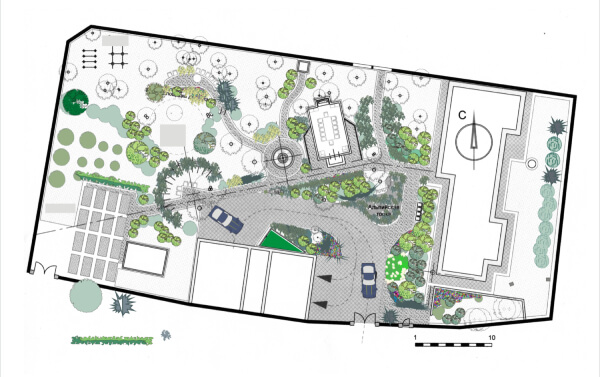
The plot layout, a key component of the plot plan, focuses on the design and arrangement of features within the property.
While a plot plan provides technical details and measurements for regulatory purposes, the plot layout emphasizes the overall organization and functionality of the land (similar to the land layout).
It illustrates how elements such as buildings, landscaping, driveways, and utilities are positioned in relation to each other to maximize both aesthetic appeal and practical use.
This aspect of the plot plan is especially useful during the design phase, helping designers and developers visualize how the space will be utilized and draft the plot plan to ensure it meets both functional and aesthetic goals.

On average, a plot plan costs around $500 due to the need for a land surveyor to measure and mark the accurate land dimensions. However, for more complex surveys, the price can increase to as much as $1,200 (see our article to learn the difference between a Land Survey and a Plot Plan).
Alternatively, you can handle the entire process yourself, from taking measurements to drawing the plot plan. Even though free, this approach can be a time-consuming and challenging task.
Lastly, a plot plan can cost as little as $89 if you opt to pick a redraw service. A team of professionals can accurately delineate property measurements with survey precision and deliver a finalized basic plot plan within 24 hours.
Yes, a plot plan shows elevation. Contour lines represent changes in elevation, with closely spaced lines indicating steep terrain.
If you can’t find the ILC (improvement location certificate), the individual preparing the plan must begin from scratch by taking measurements or getting a land survey. Once the plot plan is submitted to the local permit agency, a copy may be retained on file for future reference or use.
Yes, a plot plan can be modified after approval, but the process usually requires submitting a revision for review. Depending on the extent of the changes, additional approvals or permits may be needed, particularly if the modifications affect zoning compliance or building codes.
Given its significance, a plot plan is essential for any project on your property. A well-prepared plan ensures that your project is properly organized and meets all necessary requirements.
Taking a careful and professional approach can save you from potential setbacks or delays during construction.
To streamline the process and avoid unnecessary complications, it’s wise to rely on experts who can quickly create a plot plan with precision and accuracy.
References:
https://phoenix.municipal.codes/ZO/613
Learn more about our contributor:

Contributing Writer | Architecture & Design Writer
During my career, I’ve written articles on interior design, home remodeling, and renovation with an emphasis on money-saving tips and DIY ideas. It’s been a rewarding journey and I am thrilled to continue helping others bring their architectural visions to life.

A landscape rendering gives you a 3D preview of your garden or yard – a chance to see every angle before any work begins. And it has gone digital. What
Every year, thousands of property owners face costly delays or outright rejections because their subdivision plan requirements weren’t met. From drainage miscalculations to missing zoning data, one overlooked detail can

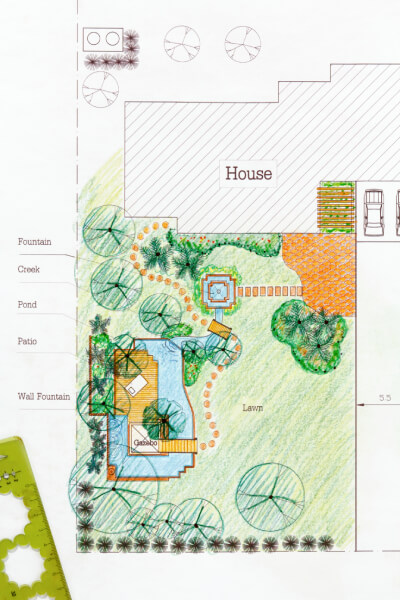
The best landscapes don’t happen by accident – behind every beautiful yard is a smart design idea that brings plants, pathways, and structure together with intention. This curated collection highlights