How to Obtain a Subdivision Site Plan for My Property (7 Ways)
If you’re a property owner planning to build, make improvements, or divide your land, one of the first things you’ll need is a subdivision site plan. However, navigating the process

Contributing Writer | Architecture & Design Writer
A residential site plan is essential for any kind of home project, from remodeling projects to new builds.
A detailed residential site plan helps you visualize and outline your property’s layout, allocate resources, and align future modifications, reducing the risk of development errors.
Read on to learn about residential site plans’ structure, design, and cost, see examples, and understand how they differ from house site plans.
Table of Contents
Toggle
A residential site plan is a detailed and scaled drawing showing the layout of a property and all the important components that exist within the property’s boundary.
It’s a type of site plan showing how a house or residential building is positioned on a piece of land while considering infrastructure and topographic features.
In other words, residential site plans provide a comprehensive view of the property for planning, permits, and proposed changes to the property.
You need a residential site plan to ensure the project complies with local zoning laws and is correctly graded and aligned with building codes and other regulations.
Typically, you’ll need a residential site plan when:
For a residential site plan to meet requirements, it must include all the key elements necessary for accuracy and compliance.

A residential site plan should include all the necessary elements that will make a comprehensive plan and provide a clear picture of how the property will be used, ensuring compliance with local regulations (as permits are required for residential site plans).
Here are the elements that need to be included in a residential site development plan (remember this may vary from place to place as zoning regulations impact how residential planning should be structured):

With all these essential details—though less extensive than those in a commercial site plan—you may now be wondering how to create and who can design a residential site plan.

Anyone with a basic knowledge of technical drawing or usage of residential site plan software can learn how to draw a residential site plan.
Bearing this in mind, if you’re unable to obtain a site plan, creating and drawing residence site plan options are:
Let’s see each option in more detail.
If drawing a residential site plan doesn’t require professional expertise and accuracy for permits, some homeowners may opt for a DIY solution, investing time to learn how to draw a site plan.
DIY methods offer the adaptability for future changes and can be cost-effective but, as mentioned above, may lack the approval-ready and code-compliant precision required for official documentation.
Nevertheless, once you familiarize yourself with the necessary rules and techniques, creating a customizable plan can be done either by hand or using some of the best software specialized for site plan drawing.
Ensure you evaluate the position of various structures to meet local zoning requirements.
You’ll also need to submit your completed residence site plan to the local zoning department for approval, which may take anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
Note: Once approved, the residential site plans can be altered, but any changes will depend on the nature of the modifications and local regulations.
For complex and large-scale projects, hiring professionals like architects or engineers is common. They ensure your site plan meets all local regulations and includes detailed specifications.
However, these services can be costly—particularly for residential site plans, where certified plans are often not mandatory.
GetASitePlan is another, probably the most resource-efficient solution for all your residential site plan needs—whether you need a new residence site plan created from scratch or an existing one redrawn for accuracy or compliance.
In both cases, GetASitePlan delivers a regulated and expertly crafted site plan for permits within 24 hours, ensuring your project meets all requirements seamlessly. Check the prices.

Residential site plan costs range from as little as $10 up to $1,200, depending on factors like location, project complexity, and the drawing option selected.
DIY options for residential site planning may only cost software fees (but require time to learn), while professional plans can cost from several hundred to thousands of dollars, especially if they include detailed landscaping or utility layouts (learn the differences between Site Plan and Survey by reading our article).
For a budget-friendly and efficient alternative, consider an online redraw service like GetaSitePlan. This option provides professional-quality plans within 24 hours, allowing you to move forward quickly.
Lastly, the price may depend on the type of residential site plan.

Residential site plans generally come in two visual formats: 2D and 3D.
Both 2D and 3D residential site plans can be landscaped to highlight specific areas and include precise grade specifications, offering a well-managed overview of your property’s layout and accessibility.
Here are the main characteristics of each one:
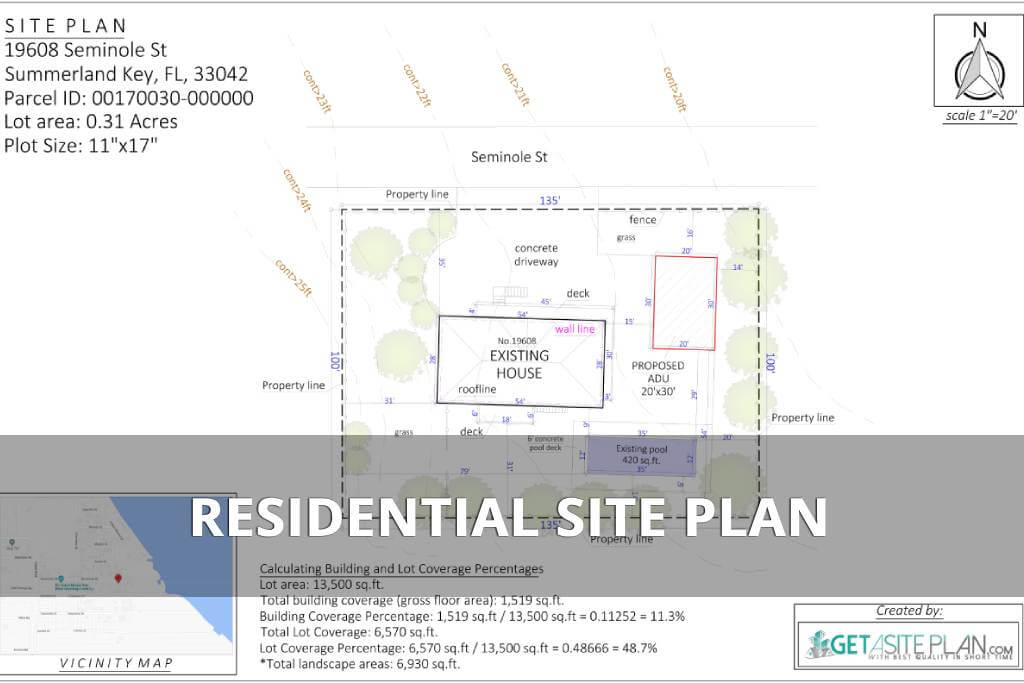
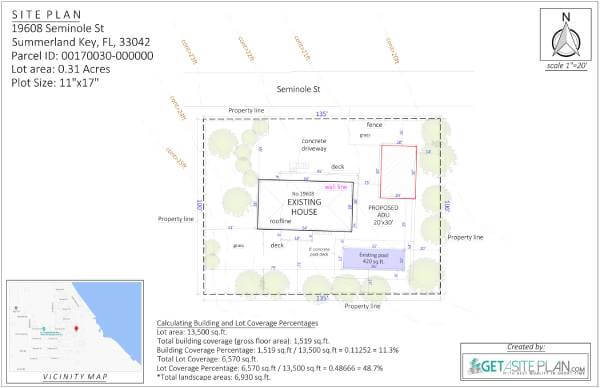
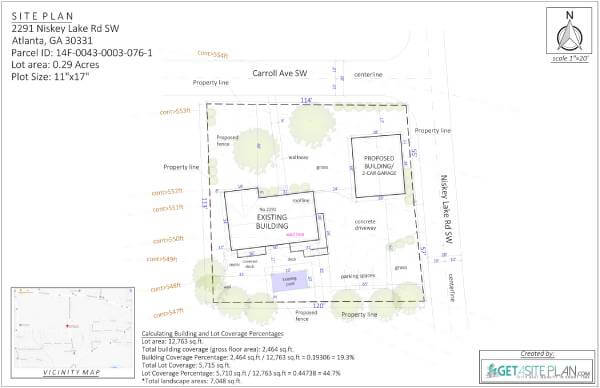
Below are examples of 2D residential site plans, as these are more commonly used.
These site plan examples show efficient layouts with features that enhance accessibility and property usability.
If you would like to get a full understanding of residential site plan drawing features and symbols, you can read the How to Read a Site Plan article.
In the two examples below, you can see how residential site plans provide homeowners with a complete view of their property, showing how the house and any new structures—whether attached or detached—will look once built.
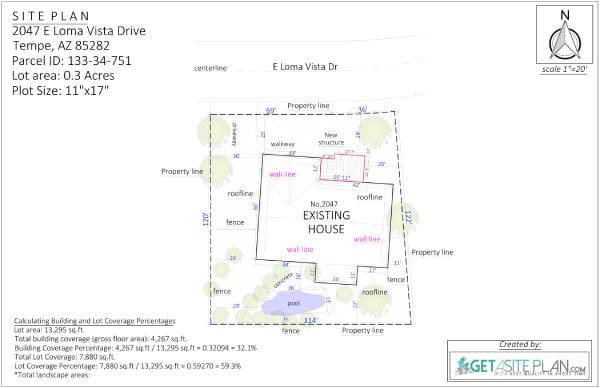

House site plans are primarily focused on the layout of a single building (house or residential building) on a property.
The site plan of the house shows how the building sits on the lot, detailing the house’s footprint, orientation, and relationship to other property features, usually without extensive information about other site elements.
The property features usually included in site plans of houses are:
Overall, home site plans prioritize optimizing the specific house design within its lot. An accessible utility layout is crucial for ease of maintenance and future additions.
Since it has a lot in common with a residential site plan, the section below talks about the main differences between the two and how to differentiate them.
The main difference between a house site plan and a residential site plan is that a residential site plan covers the entire property, while a house site plan is generally limited to the immediate area surrounding a single building.
This means that a residence site plan includes landscape and utility details, while a site plan of a house is more narrowly focused on the building footprint.
Here’s a table showing the differences between home site plans and residential site plans.
| Aspect | Residential Site Plan | House Site Plan |
| Scope | Entire property layout, covering land and structures | Primarily focused on the house itself |
| Focus on exterior | Yes, includes driveways, landscaping, and boundaries | No, mostly the internal layout of the house |
| Property boundaries | Shown and essential | Typically not included or simplified |
| Utilities and Connections | Covers all connections entering/exiting the property | May only cover internal plumbing and electrical |
| Topography and Drainage | Often included to show slopes and water flow | Rarely included |
| Zoning and Setbacks | Highlights building restrictions related to property boundaries | Usually not a focus |
| External Features | Includes features like fencing, patios, and outbuildings | Rarely included, if at all |
| Interior Details | Minimal to none | Comprehensive, covering rooms, walls, and fixtures |
And since a housing site plan is primarily focused on a single house, what separates it from a floor plan?

The main difference between a house site plan and a floor plan is in what they show and the level of detail.
House site plans are site-specific and show the home’s placement on the lot and its exterior features. This scalability makes a house site plan adaptable to varied topography and landscape design adjustments.
On the other hand, floor plans focus on the interior layout of the home, which means that floor plans include rooms, walls, windows, and doors. They provide the house view from above, without external property features.
These factors, along with a few others, are what distinguish floor plans from site plans as well.
A well-designed residential site plan is essential for a successful project.
It provides key details that ensure efficient use of space, compliance with regulations, and a solid foundation for quality construction.
By securing a precise, professional site plan, you’re already halfway to completing your project with confidence.
With GetASitePlan’s fast, 24-hour turnaround for residential site plans for permits, there’s no reason to delay starting your project.
References:
1. https://ngmdb.usgs.gov/topoview/viewer/#6/40.889/-93.417
Learn more about our contributor:

Contributing Writer | Architecture & Design Writer
During my career, I’ve written articles on interior design, home remodeling, and renovation with an emphasis on money-saving tips and DIY ideas. It’s been a rewarding journey and I am thrilled to continue helping others bring their architectural visions to life.

If you’re a property owner planning to build, make improvements, or divide your land, one of the first things you’ll need is a subdivision site plan. However, navigating the process

A porch is one of the most versatile and inviting parts of a home. It’s where curb appeal meets comfort, providing a place to welcome guests, relax with family, or

Plot plans and land surveys are invaluable for land ownership or development. They provide detailed insights into a property’s structure and layout. Although these terms are often used interchangeably, they